* On your first PCB Assembly order!
* Up to $300 discount
 C - A L L E Y
C - A L L E Y 
Home | Events | PCBA | About Us | News | Contact Us
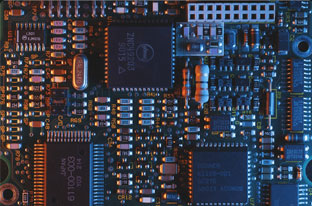
PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board, which is a conductive pattern made of printed circuits, printed components, or a combination of the two on the insulating material according to a predetermined design. The conductive pattern that provides electrical connections between components on an insulating substrate is also called a printed circuit. The finished board of the printed circuit is called a printed circuit board, also known as a printed circuit board or PCB.
PCBs are used in almost all electronic equipment, from electronic watches, calculators, general-purpose computers, to communication electronic equipment. As long as there are electronic devices such as integrated circuits, all electrical interconnections use PCBs. It provides mechanical support for fixed assembly of various electronic components such as integrated circuits and realizes wiring and electrical connection or electrical insulation between various electronic components such as integrated circuits. PCBs also provide required electrical characteristics such as characteristic impedance.
The process of making PCBs is relatively complex, and it involves a wide range of processes, from simple mechanical processing to complex mechanical processing, common chemical reactions, photochemical, electrochemical, thermochemical, and other processes, computer-aided design CAM, and many other aspects of knowledge. There are many process problems in the production process, and new problems will be encountered from time to time. Some problems disappear without finding the cause. Because the production process is a non-continuous assembly line form, any problem in any link will cause the entire line to stop production.

Introduction to PCB Printed Circuit Board
To gain a better understanding of PCBs, it's important to know the production process for the standard single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer boards.
For double-sided rigid printed circuit boards, the process involves several steps. First, a double-sided copper clad laminate is used. The blanking process is then carried out, followed by stacking the board. Next, CNC drilling through holes is performed, and the board is inspected, deburred, and brushed. The process continues with chemical plating, full board electroplating of thin copper (if required), inspection brushing, screen printing negative circuit patterns, curing (using dry film or wet film, exposure, and development), inspection, repairing, circuit pattern plating, tin electroplating (using anti-corrosive nickel/gold), and removing printing material (photosensitive film). The board is then etched copper (with the tin removed) and cleaned and scrubbed. Next, the solder mask graphics are screen-printed, commonly using thermal curing green oil. The board is cleaned and dried, and the character graphics are screen-printed and cured. The board undergoes shape processing, cleaning, drying, and electrical on-off tests before inspection, packaging, and finally leaving the factory.
The process for manufacturing multilayer boards involves the through-hole metallization method. The process starts with double-sided cutting of inner copper clad laminate, followed by brushing, drilling positioning holes, and sticking photoresist dry film or coating photoresist. It then involves exposure, developing, etching, and removing film, inner layer roughening, deoxidation, inner layer inspection, outer layer single-sided copper clad circuit production, B-stage bonding sheet, board bonding sheet inspection, drilling positioning holes, lamination, number control drilling, hole inspection, hole pretreatment and electroless copper plating, thin copper plating on the whole board, plating inspection, sticking photo-resistance electroplating dry film or coating photo-resistance electroplating agent, surface layer bottom plate exposure, developing, repairing board, circuit pattern plating, tin-lead alloy electroplating or nickel/gold plating, film removal and etching, inspection, screen printing solder mask or photo-induced solder mask graphics, printing character graphics, hot air leveling or organic solder mask, CNC washing shape, cleaning, drying, electrical on-off detection, finished product inspection, packaging and leaving the factory.
One side is for inserting components, and the other side is for component pin soldering. The solder joints are very regular, and the discrete soldering surface of the component pin is called a pad. Other copper wire patterns are not tinned, except for the soldering pads and other parts, which have a solder mask that is resistant to wave soldering. Most of the solder masks on the surface are green, while some use yellow, black, blue, etc. Solder mask oil is often called green oil in the PCB industry. Its function is to prevent bridging phenomenon during wave soldering, improve soldering quality, and save solder. It's also a permanent protective layer for printed boards, which can prevent moisture, corrosion, mildew, and mechanical scratches. The smooth and bright green solder mask is a photosensitive and thermally cured film on the board. It not only improves appearance but also makes the pads more accurate, thereby improving the reliability of the PCB.
Why Choose China PCBA Supplier KSPCBA as Your Introduction to PCB Printed Circuit Board Manufacturer?
– Experienced and skilled team
– State-of-the-art equipment
– Strict quality control
– Excellent customer service
– Competitive price
Please send Email to kspcba@c-alley.com or call us through +86 13828766801 Or submit your inquiry by online form. Please fill out below form and attach your manufacturing files( PCB Gerber files and BOM List) if need quotation. We will contact you shortly.
 +86 13828766801
+86 13828766801 kspcba@c-alley.com
kspcba@c-alley.com https://www.kingshengpcba.com/
https://www.kingshengpcba.com/ 2/F, Building 6, Tangtou 3rd Industrial Zone, Tangtou Community, Shiyan Town, Baoan District, Shenzhen, China, 518108
2/F, Building 6, Tangtou 3rd Industrial Zone, Tangtou Community, Shiyan Town, Baoan District, Shenzhen, China, 518108