
* On your first PCB Assembly order!
* Up to $300 discount
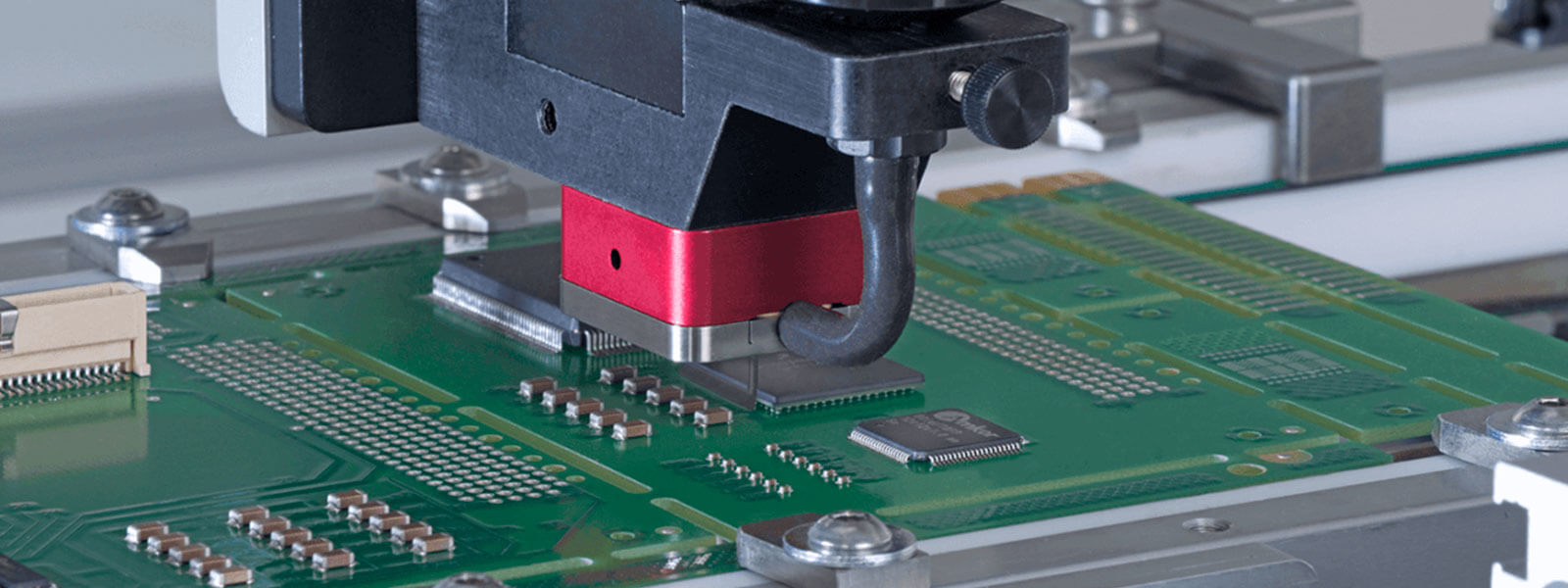
Underfill is a type of epoxy material used to fill the gap between Ball Grid Array (BGA) components and Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). BGA components are commonly used in electronic devices, and they have a large number of solder balls on the bottom surface that make contact with PCB pads. Under-fill material is dispensed onto the PCB, and it flows into the gaps between the BGA component and the PCB during the curing process.
The purpose of Under-fill is to improve the reliability and durability of electronic devices by strengthening the mechanical bond between the BGA component and the PCB. Under-fill also helps to prevent any damage to the solder balls due to mechanical stress or environmental factors like temperature changes.
There are different types of Under-fill materials available, each with their unique properties and characteristics. Some Under-fill materials are designed to be cured using heat, while others can be cured through UV light exposure. The choice of Under-fill material depends on several factors such as the operating environment of the electronic device, required thermal performance, and cost considerations.
Underfill methods are the techniques used to apply Underfill material to Ball Grid Array (BGA) components on Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). Here are some common Underfill methods:
This method involves using a dispensing machine to apply Underfill material to the PCB. The machine dispenses a precise amount of Underfill material onto the PCB, which flows into the gaps between the BGA component and the PCB. This method is useful in high-volume manufacturing.
This method uses capillary action to distribute Underfill material between the BGA component and the PCB. The Underfill material is applied at one end of the BGA component, and it flows through the gaps between the component and the PCB due to capillary action.
The film method involves pre-applying a thin layer of Underfill material to the PCB before attaching the BGA component. Once the BGA component is attached, the Underfill material flows into the gaps between the component and the PCB.
This method involves applying a no-flow Underfill material that solidifies into a gel-like consistency to fill the gaps between the BGA component and the PCB. This method is useful when there is limited space or the BGA component is too close to other components.
Under-fill is an essential process for improving the quality and longevity of electronic devices, especially those that are exposed to harsh environments or high temperatures.
The area around the BGA component is cleaned thoroughly to remove any contaminants that could interfere with bonding.
The Under-fill material is then heated to initiate capillary flow, which helps the material to fill all the gaps between the BGA component and the PCB.
The Under-fill material is cured either by heating at a specific temperature or through Ultraviolet (UV) light exposure, which hardens the material and improves its adhesion to the BGA component and the PCB.
After curing, the Under-filled BGA component undergoes inspection to ensure that the Under-fill has been applied uniformly and without any defects.
Kingsheng Under-fill process offers several benefits, such as improved reliability, durability, and thermal performance of electronic devices.