* On your first PCB Assembly order!
* Up to $300 discount
 C - A L L E Y
C - A L L E Y 
Home | Events | PCBA | About Us | News | Contact Us
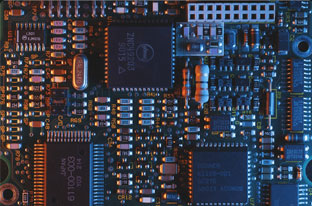
PCB circuit diagram
To ensure that a circuit diagram works properly, it must first be simulated with computer software. This software can read the design and display the circuit's operation in multiple ways, saving time and resources compared to manually building a sample PCB.
The placement of parts on the PCB is determined by how they are connected, with the goal of connecting them in the most efficient way possible. This is known as "efficient wiring," where shorter tie lines and fewer passes through layers result in less via holes. The placement of each part is crucial for perfect wiring.
Modern software can check whether each part is properly connected or can operate at high speeds, known as arranging parts. If there are issues with the circuit design, the part's position can be rearranged before exporting the line to the field.
After the connections have been made in the field, the final composition of the PCB is referred to as Artwork. Each design must adhere to specific regulations, such as minimum retention gaps between lines, minimum line width, and other practical limits. The regulations differ based on the circuit's speed, signal strength, sensitivity to power consumption and noise, and the quality of the material and manufacturing equipment. The thickness of the wire must also increase as the current intensity rises.
The final test determines if the line is functioning correctly after wiring. It checks for incorrect connections and ensures all connections align with the circuit diagram.
Manufacturers require standards-compliant files to make PCBs, with the Gerber files specification being the most common. Gerber files include a plan view of each signal, power supply, and ground plane, as well as a plan view of the solder mask and screen print surface, and designated files such as drill holes and pick and place.

Main Design Process of PCB
Electromagnetic compatibility problem
Electronic devices that are not designed to meet EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) specifications are likely to emit electromagnetic energy and interfere with nearby appliances. EMC sets limits on electromagnetic interference (EMI), electromagnetic fields (EMF), and radio frequency interference (RFI) to ensure the normal operation of the device and other nearby appliances. This regulation aims to prevent electromagnetic energy from entering or being emitted by the device.
Solving EMC issues can be difficult. Most devices use power and ground planes or put PCBs in metal boxes to reduce the magnetic susceptibility of external EMF, EMI, RFI, etc. The power and ground planes prevent the signal layer from being disturbed, and the metal box is also effective.
The maximum speed of the circuit depends on how it is designed according to EMC regulations. Internal EMI, like the current consumption between conductors, increases with frequency. If the current difference between the two is too large, then the distance between the two must be increased. This also tells us how to avoid high voltages and minimize the current consumption of the circuit. The delay rate of the wiring is also important, so the length should be as short as possible. Therefore, a small PCB with good wiring will be more suitable for operation at high speed than a large PCB.
Why Choose China PCBA Supplier KSPCBA as Your Main Design Process of PCB Manufacturer?
– Experienced and skilled team
– State-of-the-art equipment
– Strict quality control
– Excellent customer service
– Competitive price
Please send Email to kspcba@c-alley.com or call us through +86 13828766801 Or submit your inquiry by online form. Please fill out below form and attach your manufacturing files( PCB Gerber files and BOM List) if need quotation. We will contact you shortly.
 +86 13828766801
+86 13828766801 kspcba@c-alley.com
kspcba@c-alley.com https://www.kingshengpcba.com/
https://www.kingshengpcba.com/ 2/F, Building 6, Tangtou 3rd Industrial Zone, Tangtou Community, Shiyan Town, Baoan District, Shenzhen, China, 518108
2/F, Building 6, Tangtou 3rd Industrial Zone, Tangtou Community, Shiyan Town, Baoan District, Shenzhen, China, 518108